# http 和 https 协议
# 简单的面试题
- 常见的状态码
- 200 请求成功 301(永久重定向,配合 location)302 (类似短路径的跳转)临时重定向
- 304 资源未被修改 5xx 服务端错误
- 401 用户认证错误 403 用户认证后无权限 404 资源没有找到
- 常见的 headers
- request headers:
- accept 浏览器可接收的数据格式 accept-encoding 压缩算法,如: gzip cookie host
- accept-languange 语言类型 zh-CN Connection: keep-alive 一次 TCP 链接重复使用
- UA 浏览器信息 Content-type 发送数据的格式,如: application/json
- response headers:
- Content-type 返回的数据格式,如: application/json content-encode 返回数据采用的压缩算法
- content-length 返回多少字节 set-cookie 返回的 cookie
- 自定义 header
- restful api
- get 获取数据 post 新建数据 patch/put 更新数据 delete 删除数据 把 url 当成一个功能
- restful api 把 url 当作一个唯一的资源(尽量不用 url 参数,使用 method 表示操作类型)
- post /api/blog patch /api/blog/100 get /api/blog/100
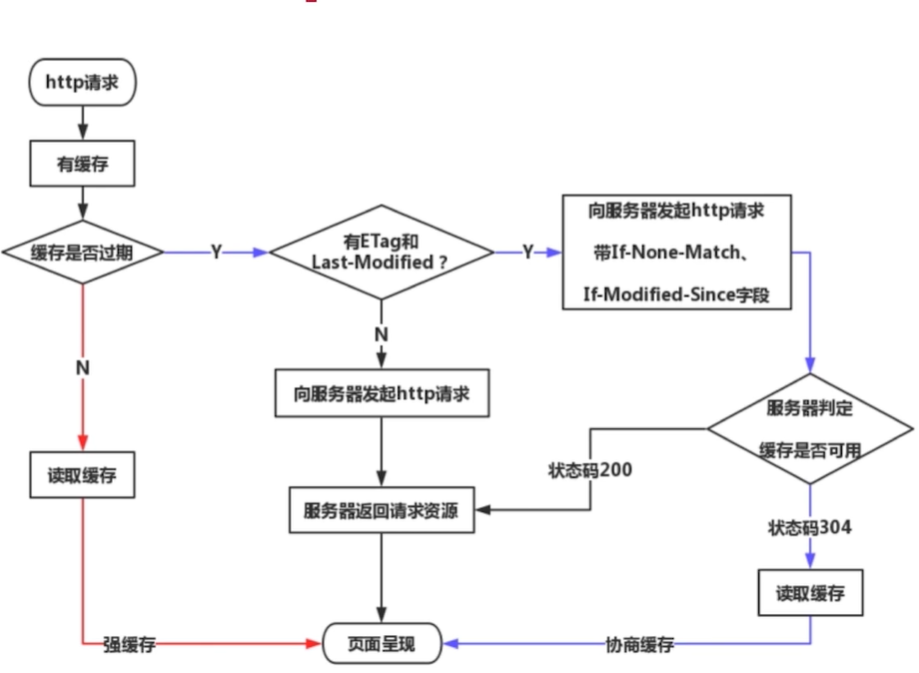
- 缓存机制
- cache-control expires
- last-modified if-modified-since
- etag if-none-match
# 缓存
- 静态资源 js css img 等
# 强制缓存
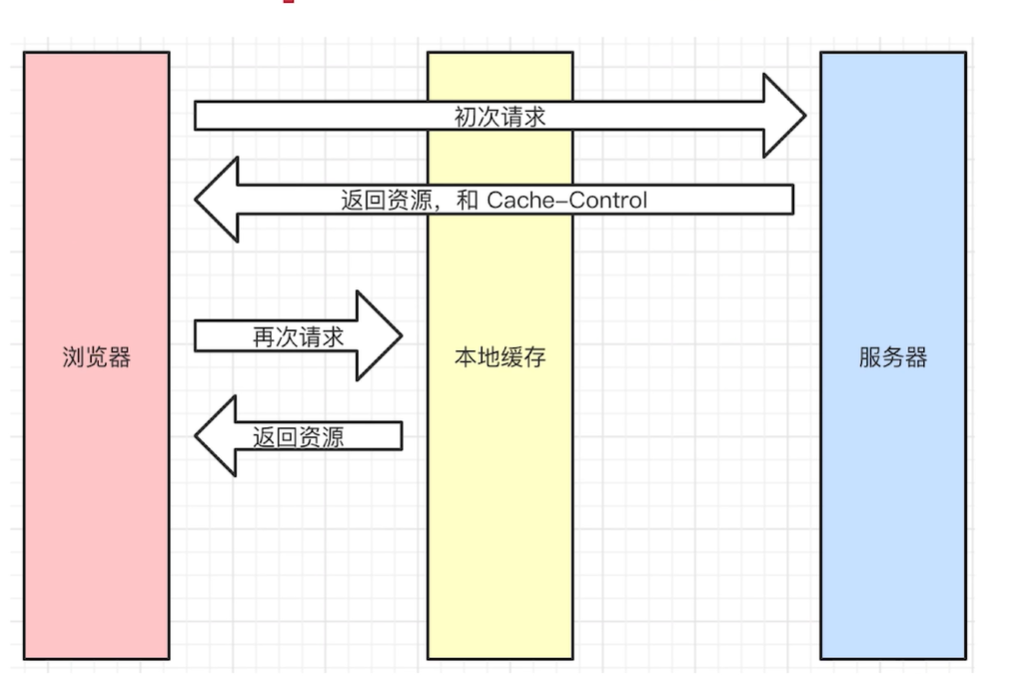
- cache-control 的值有 max-age、no-cache (不用强制缓存)
- 同在 expires 中(旧版的,被 cache-control 替代了!)
# 协商缓存(对比缓存)
- 服务端缓存策略
- 服务端会判断客户端资源是否和服务端资源一样,若一致 304 否则 200 和最新的资源
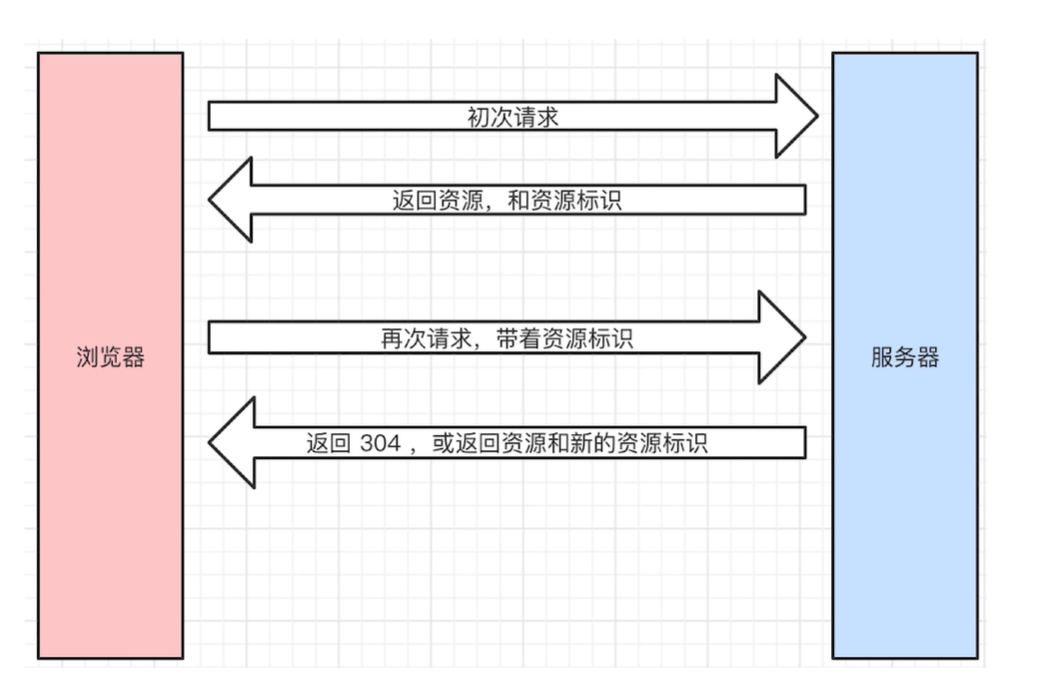
资源标识,response headers
- etag(人的指纹)
- last-modified(资源的最后修改时间)
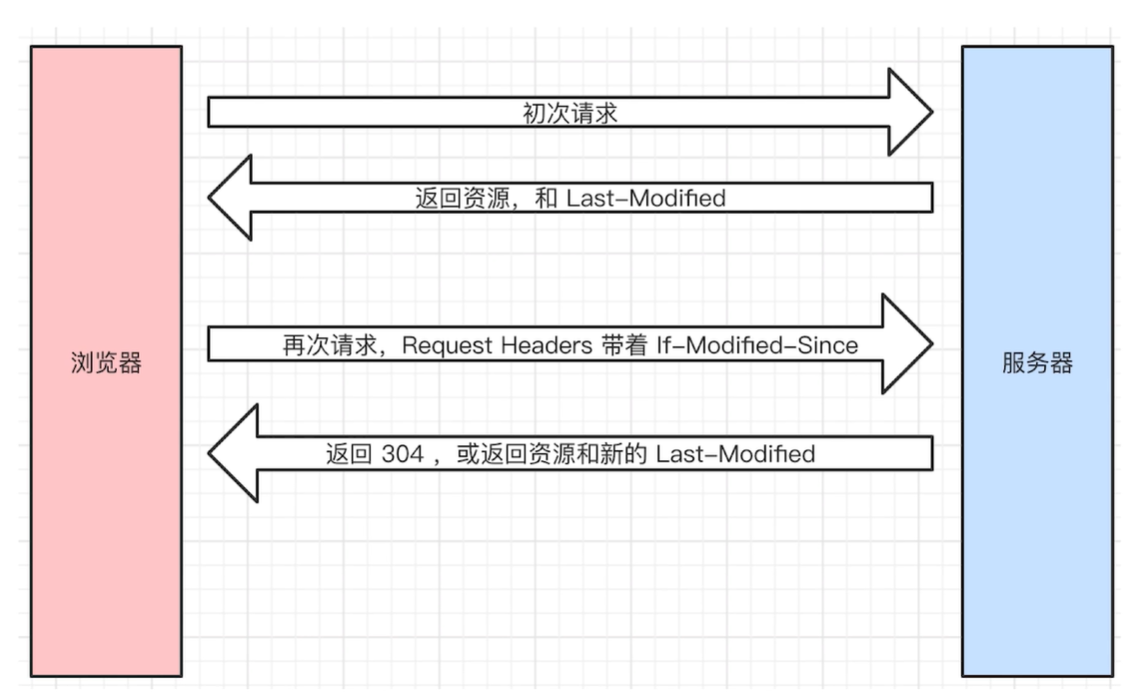
- request headers 中 if-modified-since 和 last-modified 值一样
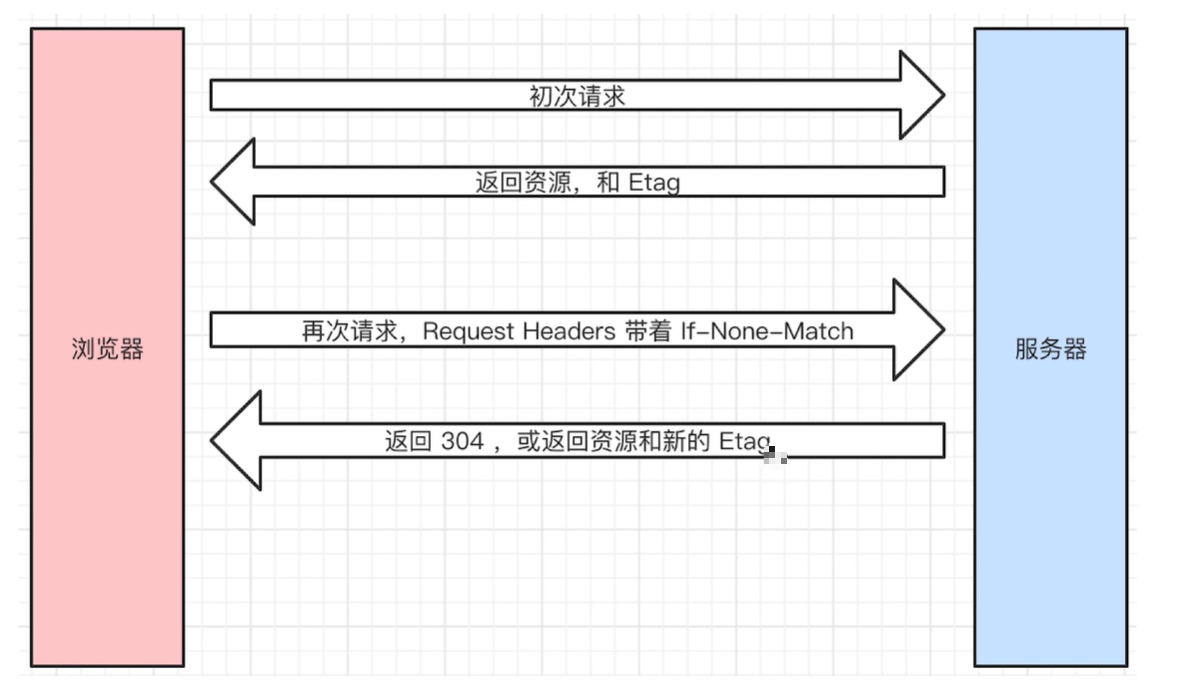
request headers 中 if-none-match 和 etag 值一样
优先使用 etag ,last-modified 只能精确到秒级,资源重复生成,内容不变,etag 更精确,是根据内容来的。
# 总结
# http https 区别
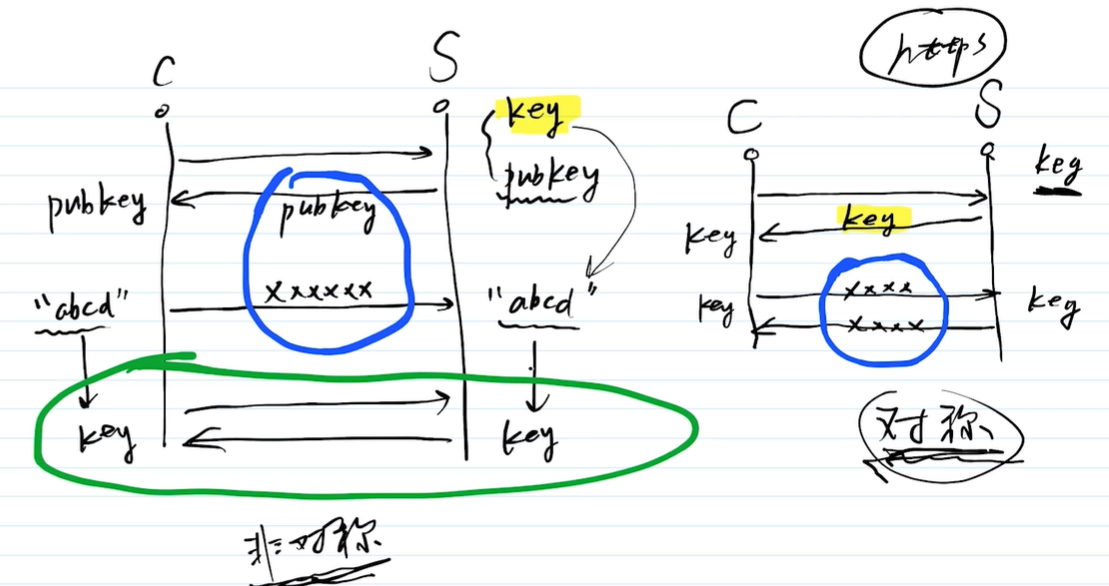
- http 明文传输,敏感信息容易被中间劫持
- https 加密,有证书,劫持了无法解密(强制 https)
加密方式:对称加密、非对称加密
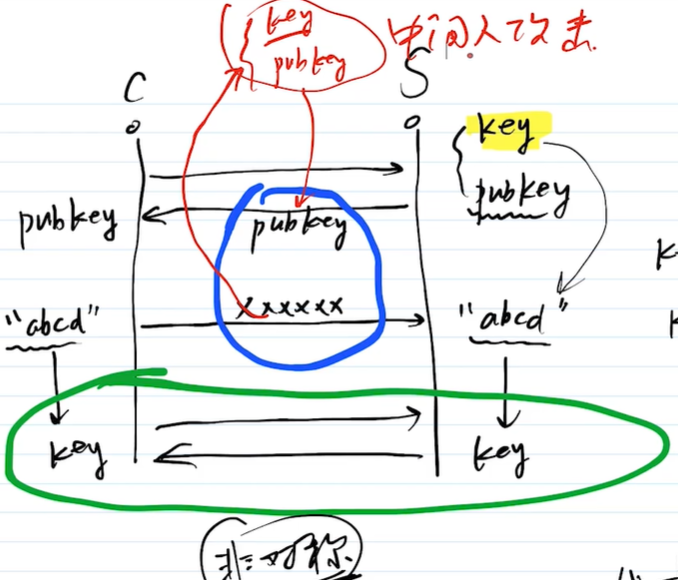
中间人攻击
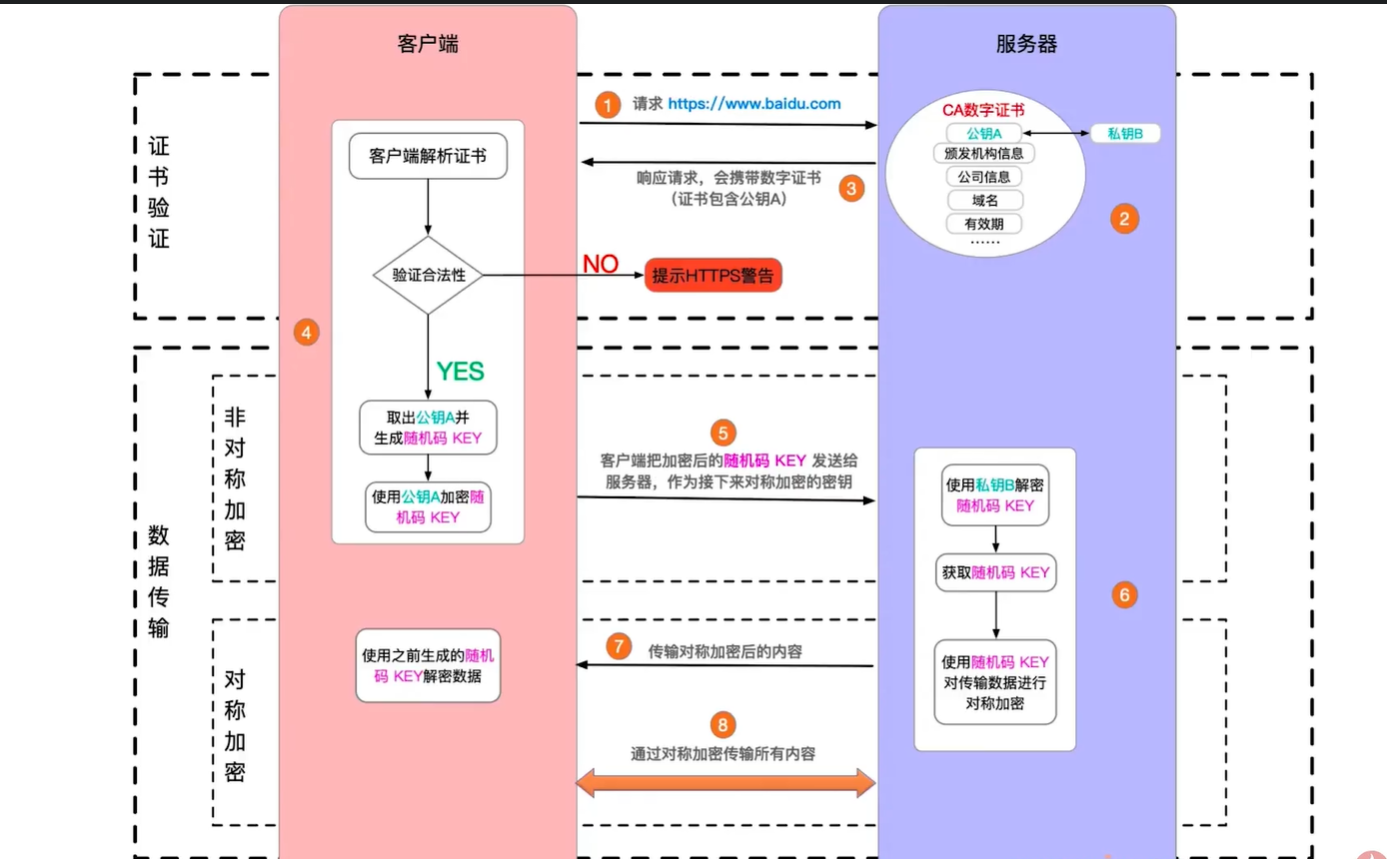
证书
- 防止被别人掉包 key + public key

# 总结
← JWT 基础